Payment Gateway vs Payment Processor

Image source: Burst
A payment gateway and payment processor are two key players in processing online payments. As an e-commerce merchant, you’ve likely heard these terms before. But what’s the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
The main difference is that a payment gateway captures and sends the cardholder's payment information to the payment processor. It also communicates approved or declined transactions to you and your customers.
Payment processors securely route data between the customer, the issuing bank, the acquiring bank, and the merchant. This happens behind the scenes in milliseconds and finishes with the settlement of funds into your bank account (as long as the payment has been approved).
This article looks deeper into the subtle differences between a payment processor and a payment gateway, how they work together, and how to choose the right provider for your business.
What's the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor?
Here’s a quick look at payment gateways vs payment processors:
Payment gateway
- Payment gateways are a type of payment service provider (PSP) that encrypts and sends payment data to the payment processor once you or the customer initiates a payment. It also notifies you or the customer of the transaction approval or denial.
- A payment gateway is primarily used to accept more payment methods through e-commerce websites, but the technology also integrates with credit card readers, mobile payment apps, and point of sale systems (POS).
📚 Further reading: How to Accept Payments Online: 6 Step Guide
Payment processor
- Payment processors send transaction data to and from the cardholder’s issuing bank and your merchant acquiring bank.
- A payment processor is required for all debit or credit card transactions, regardless of whether the sale takes place in person, via a mobile payment app, or online.
Here's an illustration to help you visualize the online payment process and how both the payment gateway and payment processor are involved:
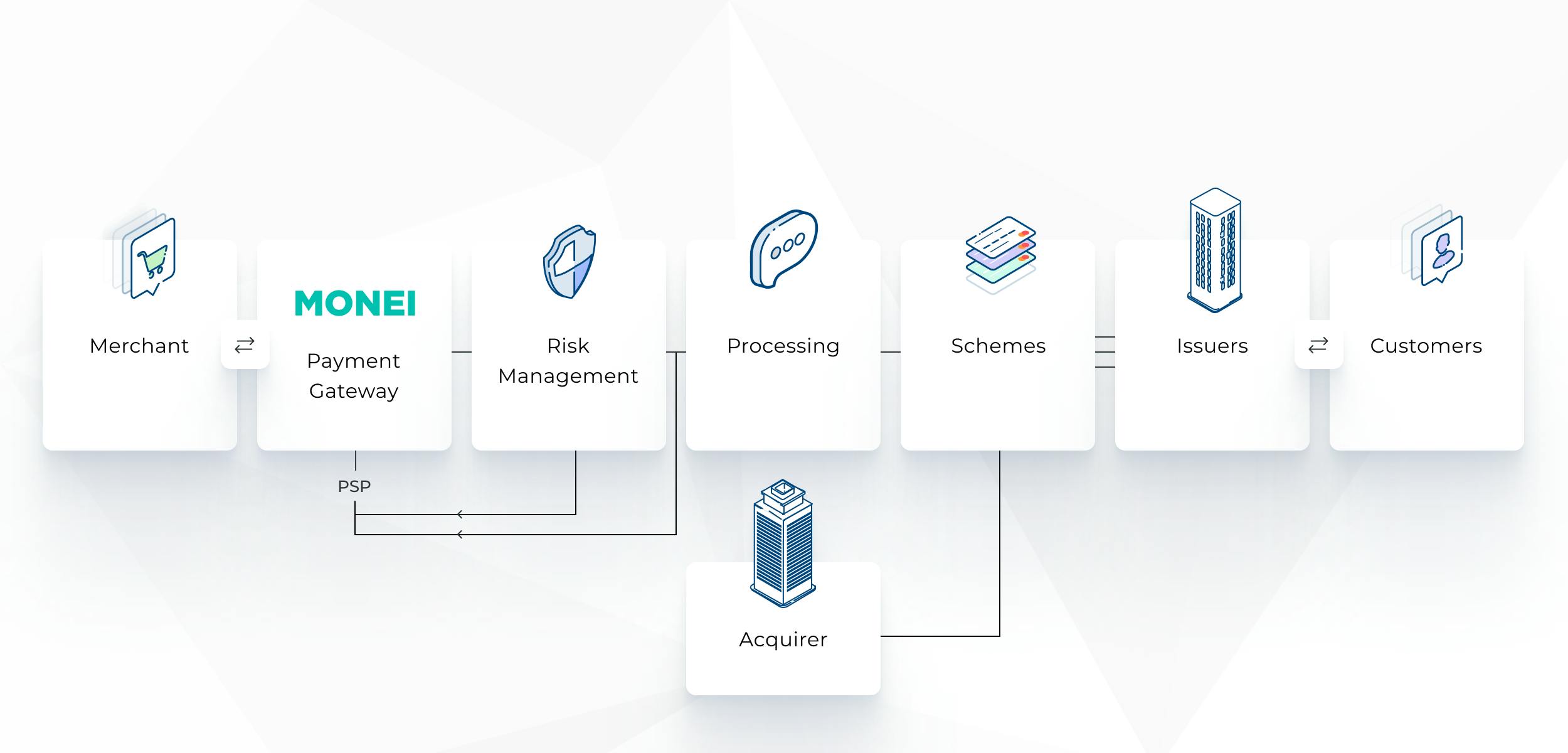
This is a great introduction, but to get a better understanding of the difference between a payment gateway and a payment processor, let’s look at the industry’s terminology and how payments work, both in brick-and-mortar and online stores:
Payment terminology
Get familiar with the terminology used in payment processing. Here are the main terms you need to know:
- Customer. The cardholder who is paying for products or services. The customer enters credit card information and initiates the transaction.
- Issuing bank. The customer’s bank that issued their credit card.
- Merchant. The business supplying goods or services for sale. This can be in-person or online.
- Merchant account. A merchant account is a special account that lets you accept and process digital payments (also known as a Virtual POS in Spain). This includes purchases made with credit or debit cards and other forms of electronic payments. But with the right payment service provider, accepting credit card payments without a merchant account is possible.
- Acquiring bank. The bank that hosts the merchant’s credit card processing account.
- Payment processor. The service that sends transaction info between the merchant, the issuing bank, and the acquiring bank.
- Point of sale (POS). A credit card processing machine at a brick-and-mortar location that reads EMV chips in credit cards and sends it through the payment processor.
- EMV chip. This computer chip is part of smart cards. EMV stands for Europay, Mastercard, and Visa, which were the three original processing firms that agreed to implement these chips in their cards. An EMV chip card generates a one-time-use transaction code that helps prevent fraud when a card is used at a point of sale.
- Payment gateway. The equivalent to a point of sale system for online transactions, it encrypts and transmits information to the payment processor. A payment gateway provides integrations into different e-commerce platforms and APIs to perform transactions. It also receives authorization for the banks to move money from the customer to the merchant.
- Payment tokenization. The process of converting the customer’s card to another number to secure their private information for the online purchase.
📚 Further reading:
What is Tokenization? And its Benefits for E-commerce
What is a payment gateway?
A payment gateway is the equivalent of a credit card terminal but it’s made specifically for online transactions. Without a card physically present, the payment gateway has to authenticate the card without help from an EMV chip. The gateway also encrypts the customer’s information to keep their bank info secure.
💡Pro Tip: Check out our guide on how to choose the best payment gateway for your e-commerce business to learn what questions to ask and factors to consider before you select a payments partner.
How does a payment gateway work?
When customers check out in an online store, they enter their payment info on the checkout page. This is where you need to have the payment gateway in place. Usually, payment gateways have easy integrations into different e-commerce platforms and developer-friendly APIs and SDKs if you want a custom integration into your own system. The gateway encrypts the data and sends it to the acquiring bank’s payment processor.
The acquiring bank sends the payment request to the issuing bank through the payment processor, and the issuing bank returns an approval or denial. If the transaction is approved, the payment gateway relays approval to the customer and closes out the sale. If 3D Secure authorization is required by the bank, the payment gateway will show a confirmation screen to the customer.
What is a payment processor?
You need a payment processor for both online and brick-and-mortar sales.
For in-person payments, a payment processor sends information between the merchant, the issuing bank, and the acquiring bank. The processor issues a brick-and-mortar business a point of sale system or a payment terminal. Payment terminals have to be able to read EMV chip cards.
There is also a payment processor for online transactions, but it works with a payment gateway instead of a physical payment terminal. The payment processor carries out the transaction once the data passes through the gateway.
📚 Further reading: A Simple Guide to Omnichannel Retail Strategy
How does a payment processor work?
When a customer uses their card in person at the payment terminal, the terminal will authenticate the card and then send the payment information to the issuing bank. The issuing bank will then approve or deny the transaction.
The payment processor will relay the approval or denial to the terminal. If the transaction is approved, the payment processor also sends the payment information to the acquiring bank.
For online transactions, the customer initiates the payment by entering their information on the payment page. The payment gateway encrypts the payment data, turns it into a token, and sends it through the processor. The processor will relay approval or denial back to the customer through the payment gateway. When the payment is approved, the processor will relay the payment information to the acquiring bank.
Payment processor vs payment gateway: do I need both?
To process online transactions, you will need both a payment gateway and a payment processor. The payment gateway is the beginning and end of the transaction, where the customer will enter their credit card information and receive an approval or denial of the transaction. The payment processor moves the information between the customer’s bank and the merchant acquirer, or acquiring bank. Every transaction processed online needs both.
Is MONEI a payment gateway or a payment processor?
MONEI is a payment gateway with built-in merchant acquiring services. This means you don’t need to work with an acquiring bank to get a Virtual POS to process card payments. All you need is one platform, and we’ll handle acquiring for you. We work with multiple payment processors, so you can set up payment routing rules using the payments orchestration feature. This way, you can approve more payments and reduce false online payment failure messages by sending transactions to more than one payment processor (in the case that a processor is experiencing downtime).
Use MONEI to improve your payment flows, accept a wider range of alternative and local payment methods, and reach more customers internationally.
📚Further reading: What’s the Difference Between a Payment Gateway and Virtual POS?
How should I choose a payment gateway and payment processor for my business?
Now that you’ve learned the basics about what goes on behind the scenes of payment processing consider what you need in a payment processor and payment gateway for your e-commerce or retail business. Depending on your current and future needs, the best option may be an all-in-one PSP that offers omnichannel payment gateway and processing services.
Here are a few factors to consider:
- Is the PSP reliable and secure? Is it PCI compliant and does it have 3DS authentication?
- Does the PSP have flexible pricing? Scaled pricing is beneficial for your business — as you sell more, your transaction fees will decrease in real-time.
- Does the PSP easily integrate with your e-commerce platform or custom-built website?
- Can you take payments online and in person?
- Does the PSP let you accept customer-preferred local payment methods?
📌 Pro Tip: Choose a powerful yet affordable payments solution for your business. Use a payment gateway that works with multiple payment processors and banks, integrates with many payment methods, and lets you accept card payments without a merchant account (i.e., without a Virtual POS). And if you already set up a Virtual POS with your acquiring bank, you can opt for the MONEI PLUS plan.
You may also like to read:
- What is a Payment Gateway? Why You Need One & How it Works
- The Top 4 Digital Wallets to Add to Your Online Store + Benefits for E-commerce
- What are Alternative Payment Methods? [Quickstart Guide]
- What is SCA? (+ How it Benefits Consumers)
- Strong Customer Authentication Guide
- PSD2: What is It? Why it’s Important + How to Be Compliant

Alexis Damen
Alexis Damen is a former Shopify merchant turned content marketer. Here, she breaks down complex topics about payments, e-commerce, and retail to help you succeed (with MONEI as your payments partner, of course).



